What is DHCP protocol
This article will help you find out everything you need to know about DHCP protocol.
What is DHCP? And why is it recommended to use it? Imagine that you work as an administrator in a large company with 500 desktop computers, and you need to set an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, DNS server and other network settings on each. How can this be done?
If you try to accomplish this task manually, you will spend a lot of time after spending 5-10 minutes on each PC, and you can, for example, accidentally enter the wrong IP address on several PCs, or even the same address on different PCs.
To solve these problems, you can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) on your network.
What is DHCP protocol
DHCP allows you to manage networks of IP addresses and other TCP / IP settings, such as DNS, default gateway, etc. from one location, this central location is called a DHCP server. In addition to management, if there are any problems, you do not need to run on the PC of your clients, you just need to connect to the server and check the DHCP settings, most likely, if there is some problem, it can be localized on the DHCP server by digging in its settings and logs.
A DHCP server can easily and completely automatically provide IP addresses to clients, so you do not need to configure and set any parameters on the client side, all you need is to configure a DHCP server, configure the scope parameters and some other protocol settings TCP / IP. You can provide your customers with IP addresses from a range of IP addresses that you choose.
Note: DHCP, in my opinion, can be called the next generation of BOOTP, because BOOTP began to be applied earlier than DHCP, and today we use BOOTP to boot over the network when deploying operating systems. In addition, DHCP was designed to work in large networks — something that BOOTP clearly cannot boast of.
How does DHCP work?
Without going into technical information (the DORA process), I will say that a DHCP client requests an IP address from the DHCP server for a while, the time for which the DHCP client received a dynamic IP address is called the lease time: rent means that the client rented the IP the address at the DHCP server for a certain time, and if the client wants to continue to use a specific IP address, he needs to renew the lease.
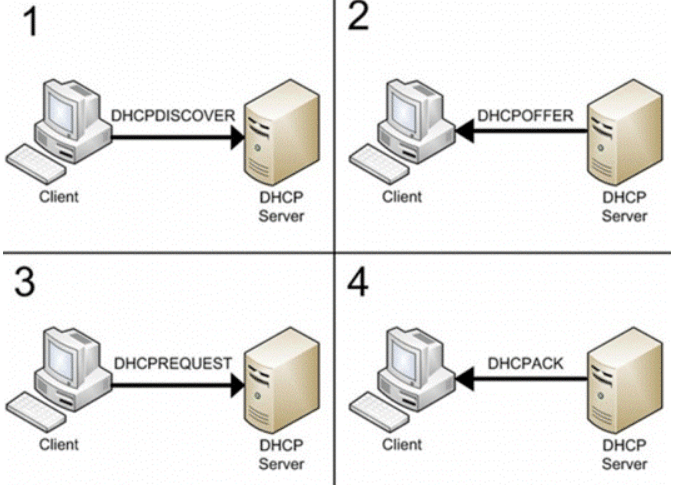
Let us analyze this process in more detail. The DHCP service works using the DORA process (Discover, Offer, Request and Acknowledgment – it can be tracked using the Network Monitor utility):
1) DHCPDISCOVER – the client sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast packet, trying to find a DHCP server on the network, in cases where a DHCP server is not on the same subnet as the client, you need to configure the DHCP Relay Agent on network devices (routers) to send a packet DHCPDISCOVER to DHCP server.
2) DHCPOFFER – the DHCP server sends a DHCPOFFER broadcast packet to the client, which includes the offer to use a unique IP address.
3) DHCPREQUEST – the client sends a DHCPREQUEST broadcast packet to a DHCP server with a response, and “asks” the server to lease out the proposed unique address.
4) DHCPACK – the DHCP server sends a DHCPACK broadcast packet to the client, in this packet the server approves the client’s request to use the IP address, and other details are also reported, such as DNS servers, default gateway, etc. If the server cannot provide the requested address or for some reason the address is invalid, the server sends a DHCPNACK packet.

Related post : Prevent domain users from join/disjoin a domain
DHCPNACK
DHCPNACK or a negative response packet, the server sends it if the IP address is already in use by another client, or the address is no longer valid.
In the case of receiving DHCPNACK, the client needs to restart the process of obtaining the lease address.
DHCP areas, exceptions and reservations
The scope (scope) of DHCP is the whole range of IP addresses that you have configured on the DHCP server, as a range of addresses, intended to be issued among clients.
For example, if you create a region with a range of issued addresses 10.0.0.100-10.0.0.200, you can easily ensure that only these addresses are issued to your workstations.
You can also create more than one area on a single DHCP server, but in this case it is recommended to check that your areas do not overlap or duplicate each other. In the process of creating such areas, you can individually configure TCP / IP parameters on clients, such as subnet mask, lease time, router (default gateway), DNS server, etc., therefore getting your address from a particular area, clients other parameters of the region are also obtained.
In some cases, you will need to prevent clients from getting some addresses, for example, if your DHCP scope has a range from 10.0.0.1 to 10.0.0.100, and the IP addresses of your servers are in the range 10.0.0.1-10.0.0.10, you will need to exclude these IP addresses from the domain that is issued by the DHC server. This possibility is called the exception (exclude).
Reservation (reservation) – is used in cases when you plan to submit a specific dynamic IP address to a specific DHCP client. For example, in your DHCP domain, you want to allocate a unique address for a specific client that will be assigned to it, for this you can easily create a reservation for it using a unique identifier – the MAC address (Media Access Control – is a unique hexadecimal physical address network adapter).
Active Directory and DHCP server
For correct operation of your Microsoft Windows DHCP server in an Active Directory environment, you must first authorize your DHCP server in AD.
In the event that an unauthorized server attempts to start the DHCP service to issue IP addresses, this start will fail and the DHCP service on the local computer will be stopped.
DHCP Relay Agent
The DHCP Relay Agent is a type of host (usually a router or server) that receives DHCP / BOOTP broadcasts from clients on subnets that do not have local DHCP servers.
DHCP Relay
The DHCP Relay Agent forwards packets from clients and DHCP servers that are located on different physical subnets, allowing them to work using the DHCP protocol, i.e. acts as an intermediary
Related post : How to rename a domain controller